依然是作为Del0n1x的密码手参赛,解了Crypto7题中的6题和1题OSINT,最终rank top 12%。
Without a Trace
task
1 | import numpy as np |
flag按照5字节一组拆分后放到了5x5矩阵
两个对角矩阵相乘的迹其实就是俩向量的的欧氏内积而已,输入
然后的oracle时,改变某个位置对应的系数为2,两次拿到的trace相减就能得到flag的5字节。
uiuctf{tr4c1ng_&&_mult5!}
X Marked the Spot
task
1 | from itertools import cycle |
得到的key只有1byte未知,直接爆破就行。
exp
1 | from itertools import cycle |
Determined
task
server.py
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes |
gen.py
1 | from SECRET import FLAG, p, q, r |
要你输入矩阵中固定几个元素的值,然后给你返回矩阵的行列式值。目标是从中拿到信息后解密一个RSA。
题目可以让我们拿到关于p,q,r的多项式,一个直观的想法是让p,q和r不同时在一项里出现。我们知道,行列式如果写成多项式形式,每一项其实是矩阵里所有既不同行也不同列的元素的乘积。所以,如果某一项里包含了和r同行/同列的元素,这一项里就一定没有r。
所以可以这么构造:
1 | # sage |
两次质询时分别令(x,y) = (1,1)和(1,2),得到的两个结果相减就消去了r,再和N做gcd就拿到了N的质因子。
b'uiuctf{h4rd_w0rk_&&_d3t3rm1n4t10n}'
Naptime
task
1 | # sage |
典型的Knapsack Cryptography,直接拿格子打就行。
exp
1 | M = [66128, 61158, 36912, 65196, 15611, 45292, 84119, 65338] |
Snore Signatures
task
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 |
问题点在于verify时的rv+m。s变化后的rv可以计算得到,然后在m里把rv的变化量抵消掉就行。
Groups
task
1 | from random import randint |
输入的数字需要经过Fermat primality test。数学上,能通过test的称为Carmichael数,wiki上给出了其子集的一种形式。
在这里我选择
1 | # sage |
*Key in a Haystack
白天忙着肝鸣潮,直到完赛前4h才开始看Crypto最后一题,所以很遗憾,虽然找到了个side-channel的方法,但没能在规定时间内解出来。(不过本来这条side-channel way也在赛中被堵了一点XDD)
对不起我的队友😭😭😭
task
1 | from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime |
朴实无华的分解质因数题目,因为有一个小因子所以赛场上我在想Pollard p-1是不是work,但是手搓了个Pollard p-1的脚本分不出那个小因子(赛后在Discord上问了下,别人用几乎一样的code是成功分解了的,但是我在赛场上试验了差不多20次没成功就跑路了😖)
然后我在本地测的时候发现这个haystack生成速度非常非常慢,但是server那里是秒出的,这时候我才嗅到一丝不对劲——server端的素数应该是预生成的。连接两次靶机后gcd了一下发现真的有非1的common divisor:
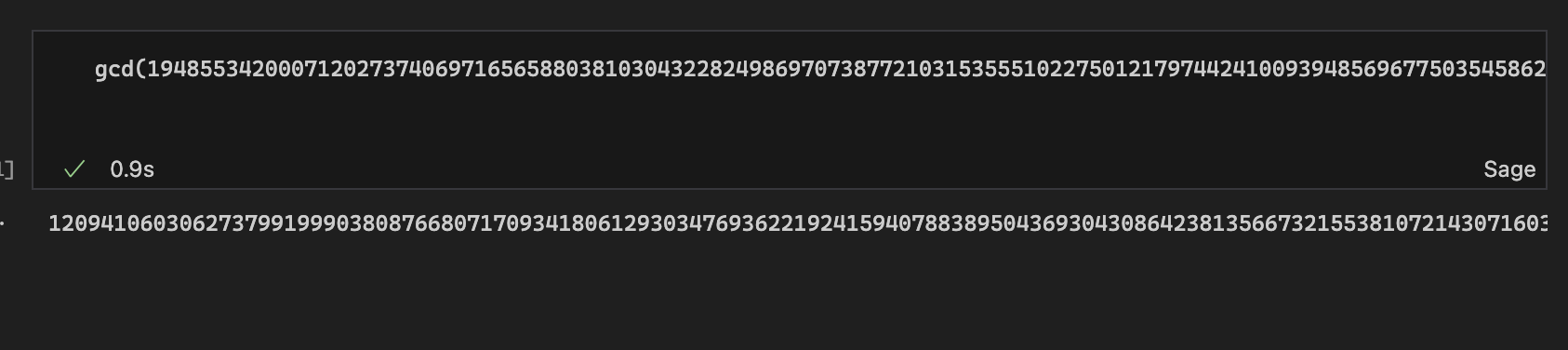
所以如果反复重连靶机+gcd应该是可以拿到它背后的完整素数表的,但是这道题有个Proof of Work,我不是很懂怎么写脚本去做,所以这条路没能走通。
但是赛后我在Discord里看到有人是走通了这条路的:
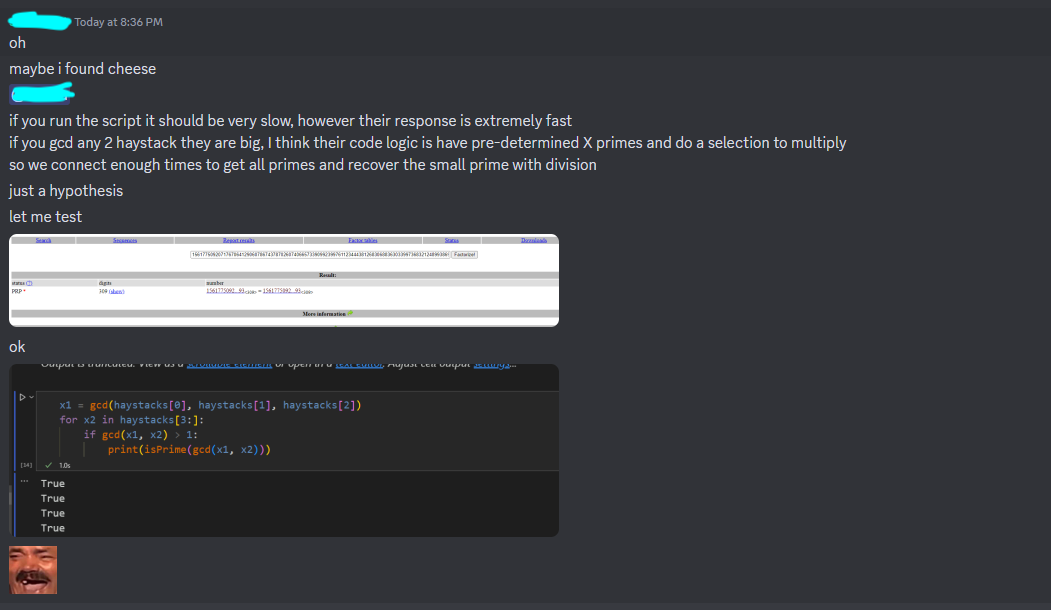
并且这道题的PoW是半途才上的:

这波只能说天时地利都没占到,所以还是精进技术吧。
我猜,预期解应该是gmp-ecm/Pollard's rho硬分?等一波官方题解。
